The Interim Budget 2024 unveils a strategic roadmap blending fiscal prudence with transformative vision for India’s railway sector. Here’s an overview of recent achievements and initiatives aimed at revolutionising Indian Railways.

Image Credit (representational): MoR
More Details:
About 94% Of Total Broad Gauge Network Of The Indian Railways Electrified:
In the last 10 years, Indian Railways has completed electrification of about 40,000 Route Km on the Broad Gauge (BG) network. There is a substantial jump in electrification from about 1.42 Km/day between 2004-14 to about 18 Km/day in 2022-23. At present, 61,813 Route km on the BG network has been electrified, which is about 94% of the total Broad Gauge (BG) network of the Indian Railways.
The electrification of the balance BG network has been taken up. During 2014-23, Rs 43,346 crore have been spent on electrification. Further, Rs. 8,070 crore have been allocated for electrification during 2023-24. As on 01.04.2023, across Indian Railways, 459 Railway Infrastructure projects (189 New Line, 39 Gauge Conversion and 231 Doubling) of total length 46,360 km, costing approx. Rs. 7.18 lakh crore are in planning/approval/construction stage.

Image Credit (representational): MoR
About 23000 Conventional Coaches Replaced By LHB Coaches Since 2015:
- Conventional (ICF) coaches are being replaced by Linke Hofmann Busch (LHB) coaches. Since 2015, about 23000 conventional coaches have been replaced by LHB coaches.
- Salient features of LHB coaches include better ride quality index, Centre Buffer Coupler for enhanced safety and anti-climbing features, Axle mounted Disc brake system, Sturdy and Robust design to minimise damage and obviating capsizing of coaches during accidents, provision of Bio-toilets, Higher Seating Capacity, Large panoramic windows, FRP (Fibre Reinforced Plastic) panels in AC coaches, Microprocessor controlled AC etc.
Status on Commissioning of Kavach:
Kavach has so far been deployed on 1465 Route km and 139 locomotives (including Electric Multiple Unit rakes) on South Central Railway. Presently Kavach tenders have been awarded for Delhi–Mumbai & Delhi–Howrah corridors (approximately 3000 Route km). The progress of main items related to Kavach is as under:
- Laying of Optical Fibre Cable : 3040 Km
- Installation of Telecom Towers : 269 Nos.
- Provision of equipment at Stations : 186 Nos.
- Provision of equipment in Loco : 170 Locos
- Installation of Track side equipment : 827 Route Km.
- Kavach system is certified for Safety Integrity Level-4. Further, the certification by Independent Safety Assessor (ISA) is conducted at the time of commissioning, once the whole section is fully equipped and tested.

Image Credit (representational): PIB
Works for provision of Intrusion Detection System to prevent accidents involving Elephants have been commissioned on 48 Route Km already identified vulnerable sections over Northeast Frontier Railway. Further, based on the vulnerability of the locations where elephant movements happen frequently over the tracks, works have also been sanctioned on Indian Railway.
The average punctuality of Mail/Express train services during 2020-21 to 2022-23 was 88.48%. Railway network on Broad Gauge has been electrified on 61508 Route Km (93.83%) up to 31.12.2023. IR has witnessed reduction in HSD consumption for Diesel locos by 44.64% in the year 2021-22 as compared 2018-19.
Consequential Train Accidents have Declined Over the Years:
Consequential train accidents have declined over the years, as shown by the graph below:
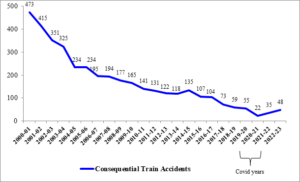
Image Credit: PIB
The average number of consequential train accidents during the period, 2004-14 was 171 per annum, while the average number of consequential train accidents during the period, 2014-23 has declined to 71 per annum. The following steps have been taken by the Government to enhance safety and to prevent train accidents:
- Rashtriya Rail Sanraksha Kosh (RRSK) was introduced in 2017-18 for replacement/renewal/upgradation of critical safety assets, with a corpus of Rs. 1 lakh crore for five years.
- From 2017-18 till 2021-22, Gross expenditure of Rs. 1.08 lakh crore was incurred on RRSK works. In 2022-23, the Govt. extended the currency of RRSK for another period of five years with Gross Budgetary Support (GBS) of Rs. 45,000 crores.
- Electrical/Electronic Interlocking Systems with centralised operation of points and signals have been provided at 6521 stations up to 31.12.2023 to eliminate accidents due to human failure.
- Interlocking of Level Crossing (LC) Gates has been provided at 11143 level Crossing Gates up to 31.12.2023 for enhancing safety at LC gates.

Image Credit (representational): RVNL
- Complete Track Circuiting of stations to enhance safety for verification of track occupancy by electrical means has been provided at 6558 stations up to 31.12.2023.
- Detailed instructions on issues related with safety of Signalling e.g. mandatory correspondence check, alteration work protocol, preparation of completion drawing, etc. have been issued.
- System of disconnection and reconnection for S&T equipment as per protocol has been re-emphasized.
- All locomotives are equipped with Vigilance Control Devices (VCD) to ensure alertness of Loco Pilots.
- Retro-reflective sigma boards are provided on the mast which is located two OHE masts prior to the signals in electrified territories to warn the crew about the signal ahead when visibility is low due to foggy weather.
- A GPS based Fog Safety Device (FSD) is provided to loco pilots in fog affected areas which enables loco pilots to know the distance of the approaching landmarks like signals, level crossing gates etc.
Modern track structure consisting of 60kg, 90 Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS) rails, Prestressed Concrete Sleeper (PSC) Normal/Wide base sleepers with elastic fastening, fan shaped layout turnout on PSC sleepers, Steel Channel/H-beam Sleepers on girder bridges is used while carrying out primary track renewals.
- Mechanisation of track laying activity through use of track machines like PQRS, TRT, T-28 etc to reduce human errors.
- Maximising supply of 130m/260m long rail panels for increasing progress of rail renewal and avoiding welding of joints, thereby ensuring safety.
- Laying of longer rails, minimising the use of Alumino Thermic Welding and adoption of better welding technology for rails i.e. Flash Butt Welding.
- Monitoring of track geometry by OMS (Oscillation Monitoring System) and TRC (Track Recording Cars).
- Patrolling of railway tracks to look out for weld/rail fractures.
- The use of Thick Web Switches and Weldable CMS Crossing in turnout renewal works.
- Inspections at regular intervals are carried out to monitor and educate staff for observance of safe practices.
- Web based online monitoring system of track assets viz. Track database and decision support system has been adopted to decide rationalised maintenance requirements and optimise inputs.
- Detailed instructions on issues related with safety of Track e.g. integrated block, corridor block, worksite safety, monsoon precautions etc. have been issued.
- Preventive maintenance of railway assets (Coaches & Wagons) is undertaken to ensure safe train operations and to keep a check on Rail Accidents across the country.
- Replacement of conventional ICF design coaches with LHB design coaches is being done.
- All unmanned level crossings (UMLCs) on the Broad Gauge (BG) route have been eliminated by January 2019.
- Safety of Railway Bridges is ensured through regular inspection of Bridges. The requirement of repair/rehabilitation of Bridges is taken up based upon the conditions assessed during these inspections.
Indian Railways has displayed Statutory “Fire Notices” for widespread passenger information in all coaches. Fire posters are provided in every coach so as to inform and alert passengers regarding various Do’s and Don’ts to prevent fire. These include messages regarding not carrying any inflammable material, explosives, prohibition of smoking inside the coaches, penalties etc.
Production Units are providing Fire detection and suppression systems in newly manufactured Power Cars and Pantry Cars, Fire and Smoke detection systems in newly manufactured coaches. Progressive fitment of the same in existing coaches is also underway by Zonal Railways in a phased manner.
Regular counselling and training of staff is undertaken. Concept of Rolling Block introduced in Indian Railways (Open Lines) General Rules vide Gazette notification dated 30.11.2023, wherein work of maintenance/repair/replacement is planned up to 52 weeks in advance on rolling basis and executed as per plan.

Image Credit (representational): North Central Railway
Increased: 1318 number of stations have been identified for development/redevelopment under Amrit Bharat Station scheme:
The Ministry of Railways has launched ‘Amrit Bharat Station scheme’ for development of Stations on Indian Railways. This scheme envisages development of stations on a continuous basis with a long term approach. It involves preparation of Master Plans and their implementation in phases to improve the amenities at the stations like improvement of station access, circulating areas, waiting halls, toilets, lift/escalators as necessary, cleanliness, free Wi-Fi, kiosks for local products through schemes like ‘One Station One Product’, better passenger information systems, executive lounges, nominated spaces for business meetings, landscaping etc. keeping in view the necessity at each such station.
- The scheme also envisages improvement of buildings, integrating the station with both sides of the city, multimodal integration, amenities for ‘Divyangjans’, sustainable and environment friendly solutions, provision of ballast less tracks, ‘Roof Plazas’ as per necessity, phasing and feasibility and creation of city centres at the station in the long term.
- So far, 1318 stations have been identified for development/redevelopment under this scheme. 1251 stations have been developed under ‘Adarsh Stations Scheme’ on Indian Railways.

Image Credit (representational): Eastern Railway
The details of allocation and expenditure for development and maintenance of stations are maintained zonal Railway-wise and not state-wise or station-wise or scheme-wise. Development of stations and provision of Passenger amenities are generally funded under Plan Head – 53 ‘Customer Amenities’. There are 02 Zonal Railways, viz. Northern Railway (NR) and North Western Railway (NWR) which cater to the State of Punjab. During the year 2021-22, 2022-23 and 2023-24 total ₹ 1148.74 Crores expenditure has been incurred under Plan Head-53 and the total allocation of the current year is ₹ 2613.36Crores.
The status of implementation of the recommendations contained in the 6th report of the Standing Committee on Railways (17th Lok Sabha) on ‘Passenger Amenities including Modernization of Railway Stations’ has been placed on the Table of both Houses of Parliament on 08.03.2021.
Conclusion:
Indian Railways continues its journey towards modernization and safety enhancement, with a strong focus on electrification, safety systems deployment, and station development. These initiatives underscore the government’s commitment to transforming the railway sector and providing passengers with a safe, comfortable, and sustainable travel experience.
Source: PIB- Press Release | Featured Image Credit (representational): MoR