Rashtriya Rail Sanraksha Kosh (RRSK) was created in 2017-18 for execution of assessed safety works with a corpus of 1 lakh crore over a period of 5 years. The projects taken up under this fund relate to track renewal, bridges, signalling, rolling stock, training and amenities for safety critical staff.
More Details:
- RRSK works are to be funded from Gross Budgetary Support (GBS) and Railways revenues/resources including mobilisation of resources through Extra Budgetary Resources (EBR), as per Ministry of Finance guidelines on RRSK. From 2017-18 till 2021-22 an expenditure of 1.08 lakh crore was incurred on RRSK works. Details of expenditure incurred is appended as Appendix-I.
- Railway Safety Fund (RSF) was created in 2001-02 initially to fund works relating to Level Crossing and Road Over Bridge & Road Under Bridge. Its scope has subsequently been expanded for capital expenditure on other safety works also.
- During the last five years, Rashtriya Rail Sanraksha Kosh (RRSK) and Railway Safety Fund (RSF) have been operated for expenditure on safety related works. Apart from this Capital Expenditure from Gross Budgetary Support, DRF and DF is made on safety related works.
- Between FY 2014-15 and FY 2022-23 the total expenditure and BE for FY 2023-24 amounts to 1.78 lakh crores on safety related plan heads. Details are appended as Appendix-II. This amount is about 2.5 times the amount spent on safety related plan heads during FY 2004-05 to FY 2013-14 (` 70,274 crore).
- Funds are provided project-wise which may fall in multiple zones/divisions, hence, zone-wise expenditure on safety works is appended as Appendix-III.
- Safety critical staff like drivers keep continuous watch on track and signals. This involves standing. Therefore, the quality of rest after duty hours is very important. To have loco pilots/assistant loco pilots well rested before the next duty, amenities like foot massager, yoga mats, fitness facilities, kitchen utensils were recommended for running rooms, in the technical report submitted by Centre for Advanced Maintenance Technology (CAMTECH) in 2013.
- Laptops and computers were also provided for safety related Track Management System application besides training of safety manpower. Hence, the expenditures were based on set guidelines for procurement of up gradation of running room and training staff etc. directly related with safety of train running.
- C&AG in its performance audit report No 22 of 2022 on “Derailment in Indian Railways” has observed that some of the expenditure booked to RRSK was in non-priority items.
- Railways has replied to the audit observation in the Action Taken Note, stating that these expenditures are covered by policy letters and technical report of CAMTECH on Running Room Facilities. Accordingly, required expenditure on equipment and gear for safety critical staff has been booked to RRSK on some Railways.
The details of number of consequential train accidents from 2000-01 to 2022-23 are given below:
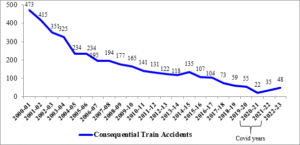
Image Credit: PIB
- As is evident from the graph above, there is a steep decline in the number of consequential train accidents from 473 in 2000-01 to 48 in 2022-23.
- The average number of consequential train accidents during the period, 2004-14 was 171.1 per annum, while the average number of consequential train accidents during the period, 2014-23 is 70.9 per annum.
The details of number of consequential train derailments from 2000-01 to 2022-23 are given below:
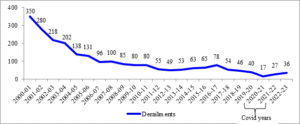
Image Credit: PIB
- As is evident from the graph above, there is a steep decline in the number of consequential train derailments from 350 in 2000-01 to 36 in 2022-23.
- The average number of consequential train derailments during the period, 2004-14 was 86.7 per annum, while the average number of consequential train derailments during the period, 2014-23 is 47.3 per annum.
The following efforts are being made by Government to prevent rail accidents:
- Rashtriya Rail Sanraksha Kosh (RRSK) was introduced in 2017-18 for replacement/renewal/upgradation of critical safety assets, with a corpus of ₹ 1 lakh crore for five years. From 2017-18 till 2021-22 a Gross expenditure of ₹ 1.08 lakh crore was incurred on RRSK works.
- Electrical/Electronic Interlocking Systems with centralised operation of points and signals have been provided at 6427 stations up to 31.05.2023 to eliminate accidents due to human failure.
- Interlocking of Level Crossing (LC) Gates has been provided at 11093 level Crossing Gates up to 31.05.2023 for enhancing safety at LC gates.
- Complete Track Circuiting of stations to enhance safety for verification of track occupancy by electrical means has been provided at 6377 stations up to 31.05.2023.
- Detailed instructions on issues related with safety of Signalling e.g. mandatory correspondence check, alteration work protocol, preparation of completion drawing, etc. have been issued.
- System of disconnection and reconnection for S&T equipment as per protocol has been re-emphasized.
- All locomotives are equipped with Vigilance Control Devices (VCD) to ensure alertness of Loco Pilots.
- Retro-reflective sigma boards are provided on the mast which is located between two OHE masts prior to the signals in electrified territories to warn the crew about the signal ahead when visibility is low due to foggy weather.
- A GPS based Fog Safety Device (FSD) is provided to loco pilots in fog affected areas which enables loco pilots to know the distance of the approaching landmarks like signals, level crossing gates etc.
- Modern track structure consisting of 60kg, 90 Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS) rails, Prestressed Concrete Sleeper (PSC) Normal/Wide base sleepers with elastic fastening, fan shaped layout turnout on PSC sleepers, Steel Channel/H-beam Sleepers on girder bridges is used while carrying out primary track renewals.
- Mechanisation of track laying activity through use of track machines like PQRS, TRT, T-28 etc. to reduce human errors.
- Maximising supply of 130m/260m long rail panels for increasing progress of rail renewal and avoiding welding of joints, thereby ensuring safety.
- Laying of longer rails, minimising the use of Alumino Thermic Welding and adoption of better welding technology for rails i.e. Flash Butt Welding.
- Monitoring of track geometry by OMS (Oscillation Monitoring System) and TRC (Track Recording Cars).
- Patrolling of railway tracks to look out for weld/rail fractures.
- The use of Thick Web Switches and Weldable CMS Crossing in turnout renewal works.
- Inspections at regular intervals are carried out to monitor and educate staff for observance of safe practices.
- Web based online monitoring system of track assets viz. Track database and decision support system has been adopted to decide rationalised maintenance requirements and optimise inputs.
- Detailed instructions on issues related with safety of Track e.g. integrated block, corridor block, worksite safety, monsoon precautions etc. have been issued.
- Preventive maintenance of railway assets (Coaches & Wagons) is undertaken to ensure safe train operations and to keep a check on Rail Accidents across the country.
- Replacement of conventional ICF design coaches with LHB design coaches is being done.
- All unmanned level crossings (UMLCs) on the Broad Gauge (BG) route have been eliminated by January 2019.
- Safety of Railway Bridges is ensured through regular inspection of Bridges. The requirement of repair/rehabilitation of Bridges is taken up based upon the conditions assessed during these inspections.
- Indian Railways has displayed Statutory “Fire Notices” for widespread passenger information in all coaches. Fire posters are provided in every coach so as to inform and alert passengers regarding various Do’s and Don’ts to prevent fire. These include messages regarding not carrying any inflammable material, explosives, prohibition of smoking inside the coaches, penalties etc.
- Production Units are providing Fire detection and suppression systems in newly manufactured Power Cars and Pantry Cars and Fire and Smoke detection systems in newly manufactured coaches. Progressive fitment of the same in existing coaches is also underway by Zonal Railways in a phased manner.
- Regular counselling and training of staff is undertaken.
- The number of Consequential train accidents has decreased from 59 in 2018-19 to 48 in the year 2022-23.
The cause of the unfortunate Balasore train accident, as reported by the Commission of Railway Safety (CRS) is as below:
- The rear-collision was due to the lapses in the signalling-circuit-alteration carried out at the North Signal Goomty (of the station) in the past, and during the execution of the signalling work related to replacement of Electric Lifting Barrier for level crossing gate no. 94 at the Station.
- These lapses resulted in wrong signalling to the Train No. 12841 wherein the UP Home Signal indicated Green aspect for run-through movement on the UP main line of the station, but the crossover connecting the UP main line to the UP loop line (crossover 17A/B) was set to the UP loop line; the wrong signalling resulted in the Train No.12841 traversing on the UP loop line, and eventual rear-collision with the Goods train (No. N/DDIP) standing there.
- Seven Railway officials have been suspended and D&AR proceedings have been initiated against these Officials.
For improving safety in train operations, Indian Railway is continuously upgrading its Signalling System to reduce the number of incidence of rail accidents:
- Provision of Electrical/Electronic Interlocking System with centralised operation of points and signals in place of old mechanical signalling. These systems have been provided at 6427 stations as on 31.05.2023, including 2173 stations in the last 05 years.
- Complete Track Circuiting of stations to enhance safety for verification of track occupancy by electrical means has been provided at 6377 stations up to 31.05.23.
- Interlocking of Level Crossing Gates (LC) has been provided at 11093 Level Crossing Gates up to 31.05.2023 for enhancing safety at LC Gate, including 1696 nos. in the last 05 years.
- Automatic Block Signalling (ABS) has been provided at 3940 route Km upto 31.05.2023, including 1006 nos. in the last 05 years.
- Indigenously developed automatic train protection system “KAVACH” has been adopted as an aid to drivers in trains running within specified speed limits and also to help the train running during inclement weather. KAVACH is being provided progressively over IR.
The details of Consequential train accidents during the last five years are given below:
| Year | Number of consequential Train Accidents |
| 2018-19 | 59 |
| 2019-20 | 55 |
| 2020-21 (Covid year) | 22 |
| 2021-22 (Covid year) | 35 |
| 2022-23 | 48 |
The Government is using the following new techniques or devices to prevent train accidents:
- With a view to provide safer and more comfortable journeys to the travelling passengers, Linke Hofmann Busch (LHB) coaches are being inducted in IR in a phased manner. Trains operating with conventional ICF coaches are getting replaced by LHB coaches in a phased manner. Around 1241 rakes are running with LHB coaches (including new introduction).
- Improved safety standards have been adopted in Vande Bharat trains, which include Train Collision Avoidance System (Kavach), Fully Sealed Gangway for Free Passenger Movement, Automatic Plug Doors, emergency openable Windows and fire extinguisher in each coach, CCTVs in all Coaches, Emergency Alarm Push buttons and Talk Back Units in all Coaches, Better fire safety- Aerosol based fire detection and suppression system etc.
- Steps have been taken to improve fire safety measures. All Power Cars, Pantry Cars and AC coaches are being equipped with suitable fire safety measures in a phased manner.
- Production Units are providing Fire detection and suppression systems in newly manufactured Power Cars and Pantry Cars and Fire and Smoke detection systems in newly manufactured AC coaches. Progressive fitment of the same in existing coaches is also underway by Zonal Railways in a phased manner.
- Technological upgradation in safety aspects of coaches and wagons, by way of introducing Modified Centre Buffer Couplers, improved suspension design and provision of Automatic fire & smoke detection system in coaches, is being carried out which would eventually lead to enhanced safety standards.
- Apart from these upgradations in Rolling Stock design and its components, Indian Railways is also installing Wheel impact Load Detectors (WILD), Hot Box Detector (HBD), Oscillation Monitoring System (OMS) etc. in a phased manner to improve safety of coaches and wagons.
- Indigenously developed automatic train protection system “KAVACH” has been adopted as an aid to drivers in trains running within specified limits and also to help the train running during inclement weather. KAVACH is being provided progressively over Indian Railways.
- This information was given by the Minister of Railways, Communications and Electronic & Information Technology, Shri Ashwini Vaishnaw in a written reply to a question in Rajya Sabha.
Source: PIB- Press Release | Featured Image Credit (representational): MoR